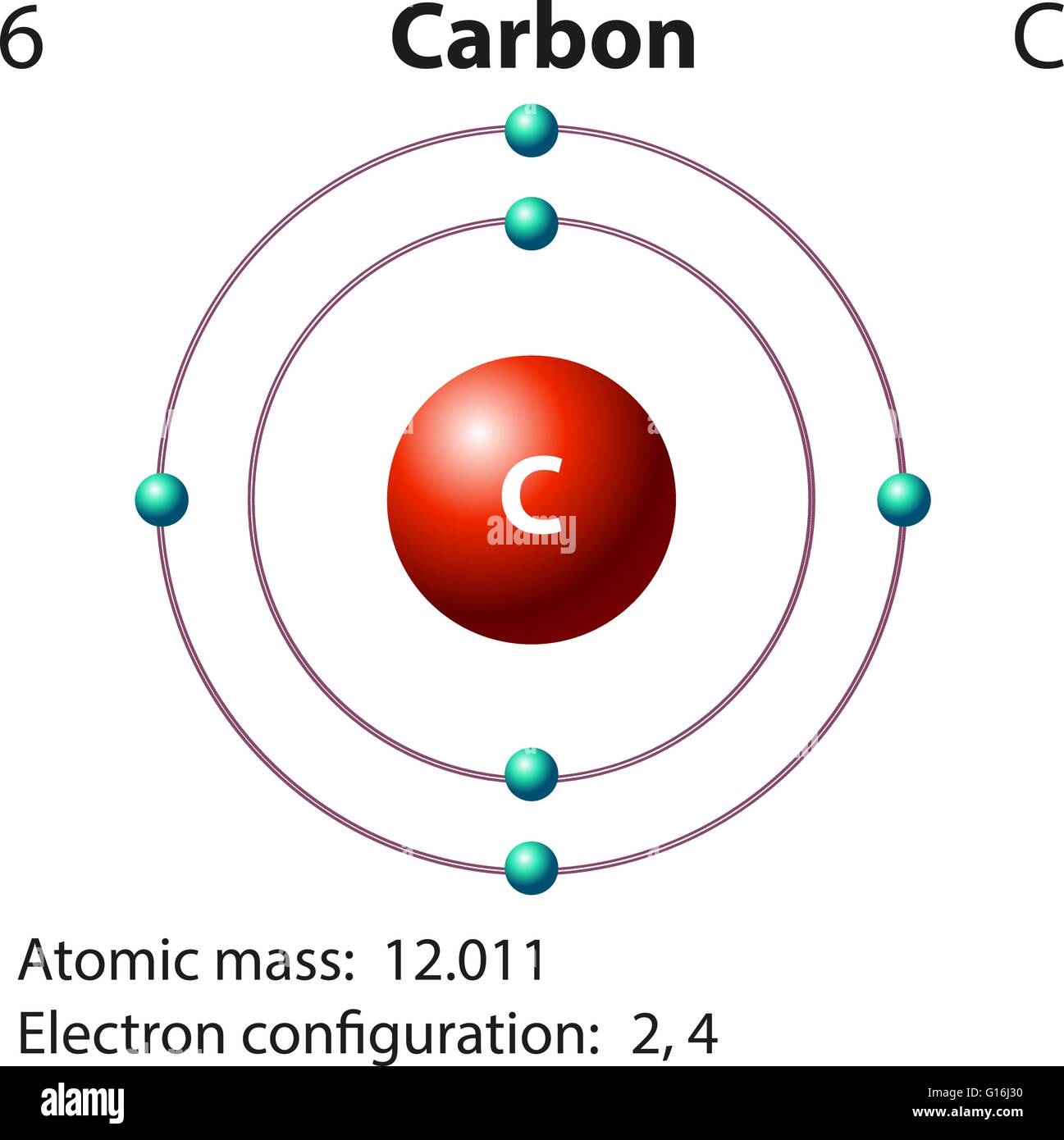
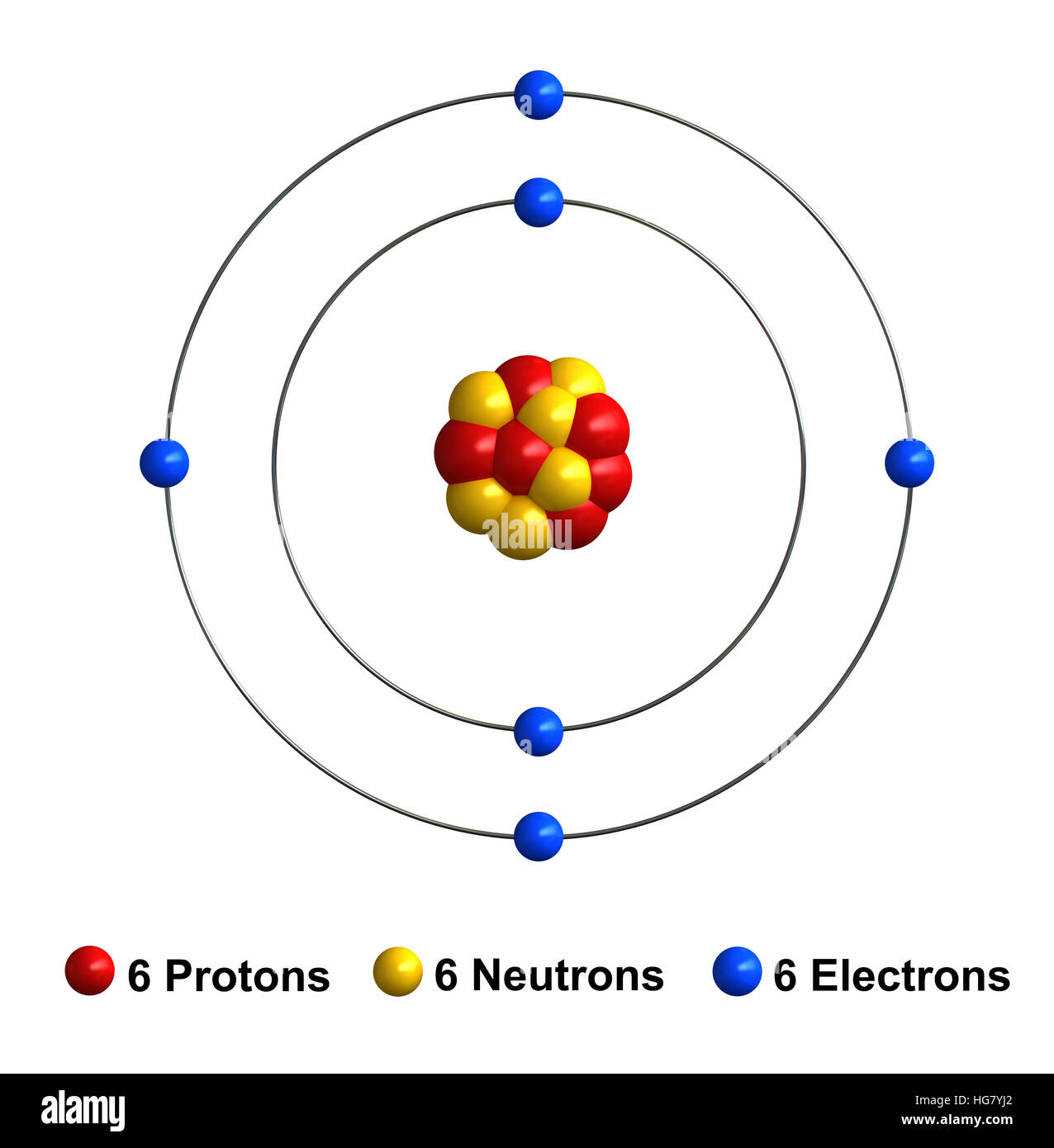
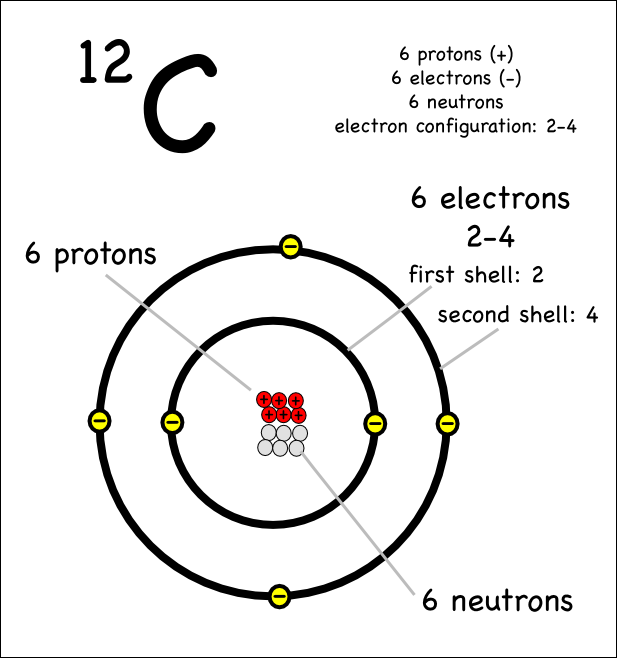
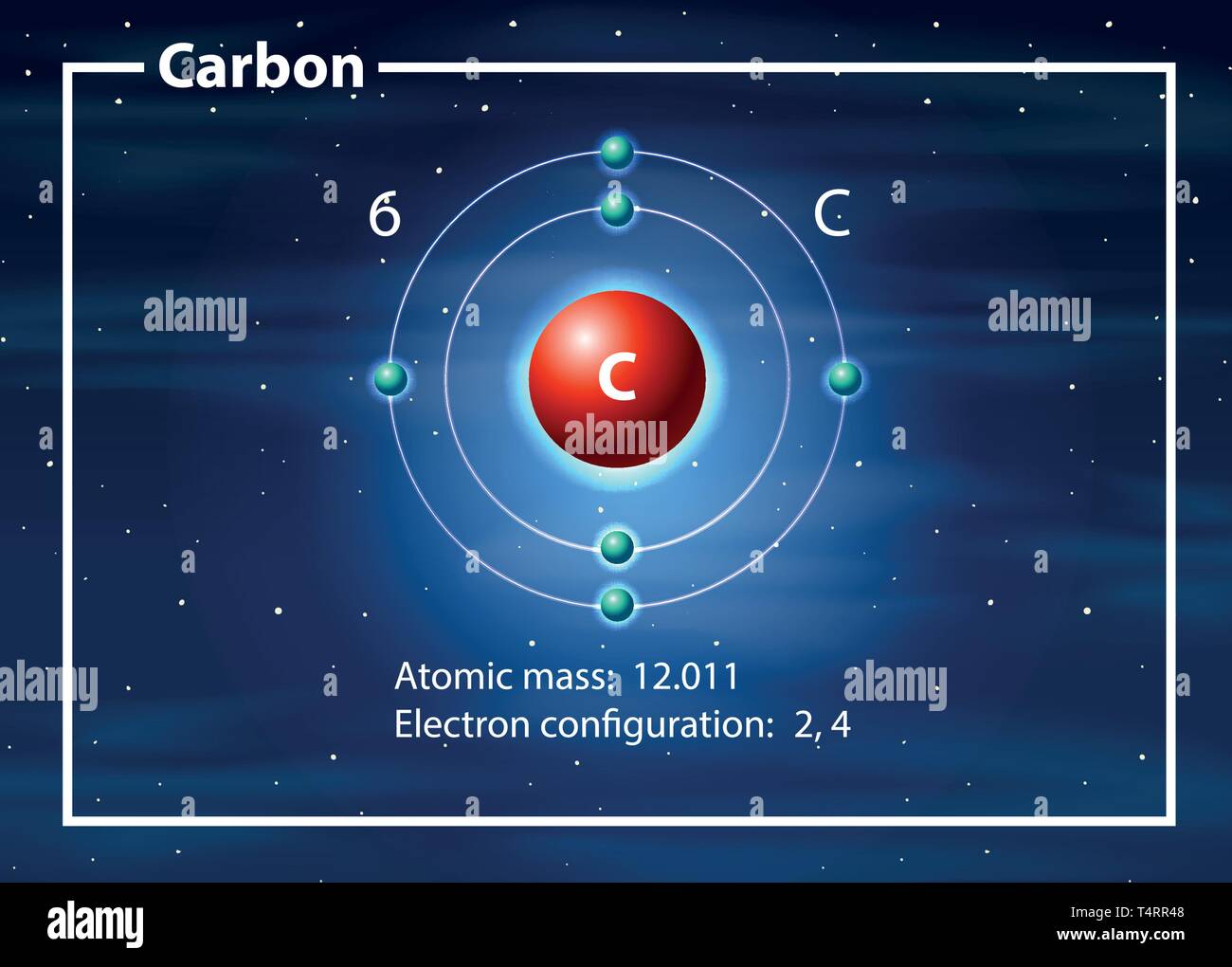
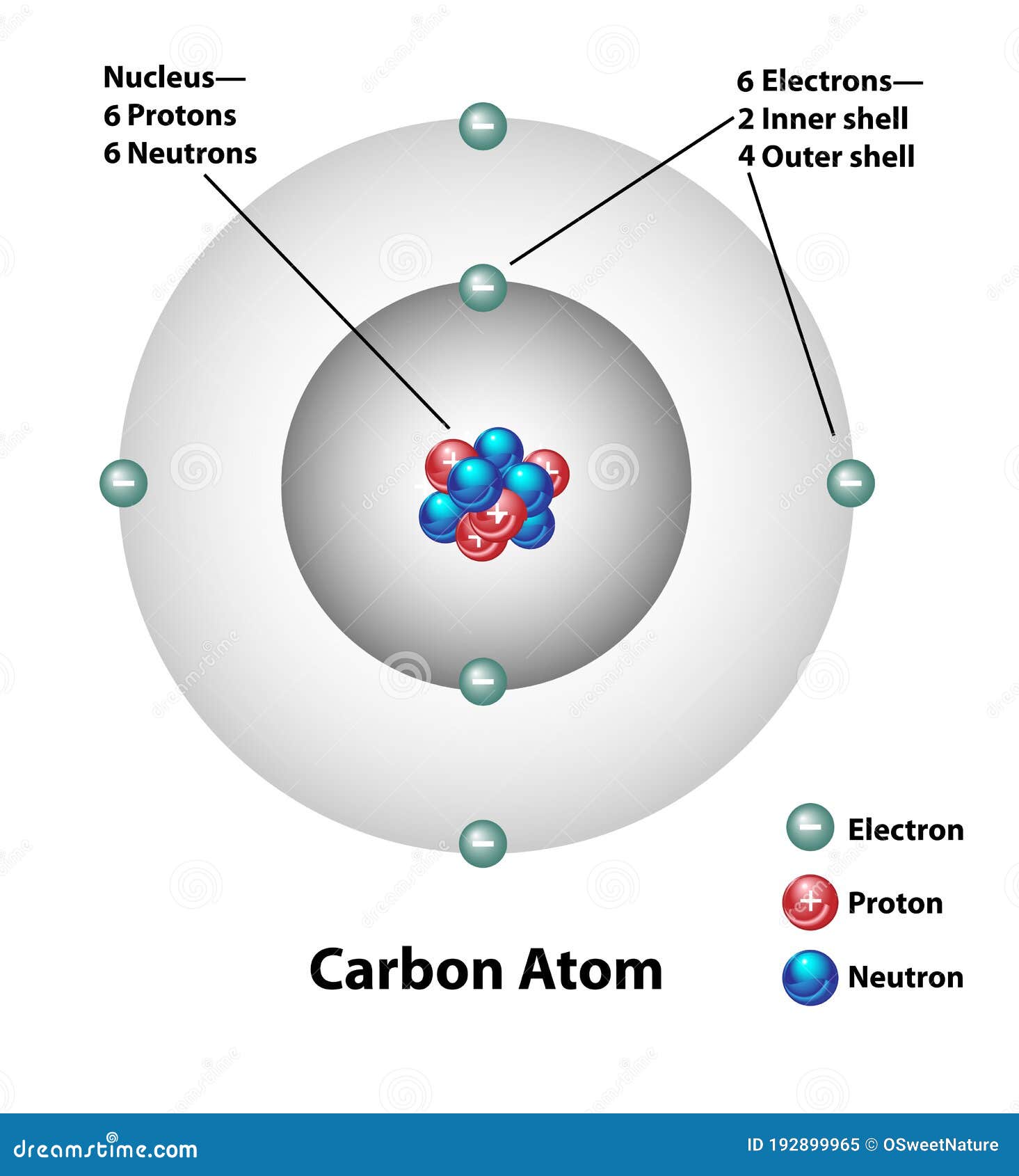
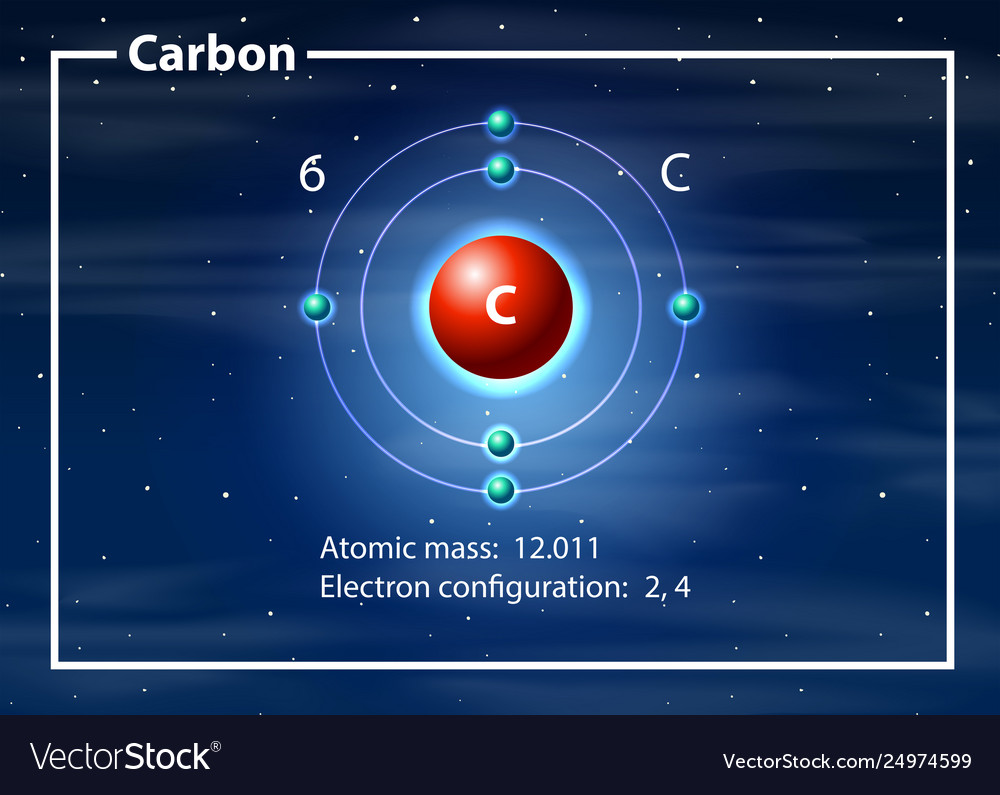
Drawing Of A Carbon Atom
Drawing Of A Carbon Atom - The carbons on top of the zigzag will have a wedge and a dash pointing towards the top of the paper. For example, consider fluorine and sulfur. Web explore the interactive simulation to build and understand atoms, isotopes, and their periodic table representations at phet. You often draw them to suit your own purposes. Web to draw the lewis structure of an atom, write the symbol of the atom and draw dots around it to represent the valence electrons. Hydrogen atoms are omitted but are assumed to be present to complete each of carbon's four bonds. As long as it’s carbon it has six protons. Click to place an atom. Web drawing every bond and every atom is tedious, however, so chemists have devised several shorthand ways for writing structures. Web a carbon atom is present wherever a line intersects another line. Web therefore, a lewis structure must be drawn for a covalent molecule before its chemical formula can be determined. Web the atomic number for carbon is 6, so you'll need 6 protons, and in turn 6 electrons. Web to draw the lewis structure of an atom, write the symbol of the atom and draw dots around it to represent the valence electrons. Web a carbon atom is present wherever a line intersects another line. Then play a game to test your ideas! Web the small grey dot that follows your cursor is an atom (carbon). Create a chain of carbon atoms. The carbons on top of the zigzag will have a wedge and a dash pointing towards the top of the paper. Carbon is still bonded to these hydrogens but we're going to ignore them for our bond line structure. Web the carbon in red is also bonded to an oxygen all right, so we need to draw in an oxygen next. Web the commonest way to draw structural formulae. Web in this video we'll look at the atomic structure and bohr model for the carbon atom (c). Pick one of the fragments (benzene, cyclopropane, etc.) and add fragments. Hydrogens that are attached to elements other than carbon are shown. In the first step, we will draw the nucleus of the carbon. Web in this video we'll look at the atomic structure and bohr model for the carbon atom (c). Web explore the interactive simulation to build and understand atoms, isotopes, and their periodic table representations at phet. Carbon is still bonded to these hydrogens but we're going to ignore them for our bond line structure. You often draw them to suit. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 electrons. We’ll use a bohr diagram to visually represent where the electrons are around the nucleus of the c. Web if you were to draw every carbon hydrogen bond in organic chemistry class it would take. Web the atomic number for carbon is 6, so you'll need 6 protons, and in turn 6 electrons. Click to place an atom. And each oxygen is six, and we have one of them, so six. Pick one of the fragments (benzene, cyclopropane, etc.) and add fragments. Converts the structural formula into a 3d model. Each hydrogen is one valence electron, but we have two of them, so 1 times 2. Carbon makes up about 0.025 percent of earth's crust. Web how to draw atoms (bohr model) in this lesson i present an overview of: Carbon is still bonded to these hydrogens but we're going to ignore them for our bond line structure. And each. Web drawing every bond and every atom is tedious, however, so chemists have devised several shorthand ways for writing structures. Web build an atom out of protons, neutrons, and electrons, and see how the element, charge, and mass change. Web explore the interactive simulation to build and understand atoms, isotopes, and their periodic table representations at phet. Hydrogens that are. Each hydrogen is one valence electron, but we have two of them, so 1 times 2. Web drawing every bond and every atom is tedious, however, so chemists have devised several shorthand ways for writing structures. Web the carbon in red is also bonded to an oxygen all right, so we need to draw in an oxygen next. Web how. Web a carbon atom is present wherever a line intersects another line. Web therefore, a lewis structure must be drawn for a covalent molecule before its chemical formula can be determined. It has symbol c and atomic number 6. Hover and click on a placed atom to place a bond. We’ll use a bohr diagram to visually represent where the. Web drawing every bond and every atom is tedious, however, so chemists have devised several shorthand ways for writing structures. Then play a game to test your ideas! Notice the carbon in red now has an octet of electrons around it. Pick one of the bond types (single, double, triple, up, down) and add or modify bonds. Converts the structural. As long as it’s carbon it has six protons. Web the small grey dot that follows your cursor is an atom (carbon). It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 electrons. Carbon is still bonded to these hydrogens but we're going to ignore them. Hydrogens that are attached to elements other than carbon are shown. For this, we will first have to calculate the number of protons and neutrons present in this atom. Web carbon (from latin carbo 'coal') is a chemical element; So, we leave those out in bond line structures. Web the carbon in red is also bonded to an oxygen all right, so we need to draw in an oxygen next. Hover and click on a placed atom to place a bond. All structures must begin with an atom. Converts the structural formula into a 3d model. Carbon is still bonded to these hydrogens but we're going to ignore them for our bond line structure. The carbons on top of the zigzag will have a wedge and a dash pointing towards the top of the paper. This atom is also balanced in charge so it also needs six electrons. Hydrogens that are attached to elements other than carbon are shown. Web there is no real right or wrong way to draw these molecules. Carbon makes up about 0.025 percent of earth's crust. Web in this video we'll look at the atomic structure and bohr model for the carbon atom (c). As long as it’s carbon it has six protons.Download Carbon, Atom, Atoms. RoyaltyFree Stock Illustration Image
Carbon atom Bohr model stock vector. Illustration of background 267661777
Carbon atom diagram hires stock photography and images Alamy
Carbon Atomic Structure High Resolution Stock Photography and Images
Drawing Atoms Montessori Muddle
Carbon atom diagram hires stock photography and images Alamy
The Carbon Atom Mind Map
Carbon Atom Molecular Structure Labels Stock Vector Illustration of
Carbon atomic structure (437243) Illustrations Design Bundles
Carbon atom diagram concept Royalty Free Vector Image
It Is Nonmetallic And Tetravalent—Meaning That Its Atoms Are Able To Form Up To Four Covalent Bonds Due To Its Valence Shell Exhibiting 4 Electrons.
Then Play A Game To Test Your Ideas!
Web Therefore, A Lewis Structure Must Be Drawn For A Covalent Molecule Before Its Chemical Formula Can Be Determined.
Web The Atomic Number For Carbon Is 6, So You'll Need 6 Protons, And In Turn 6 Electrons.
Related Post: