Draw Dna Replication
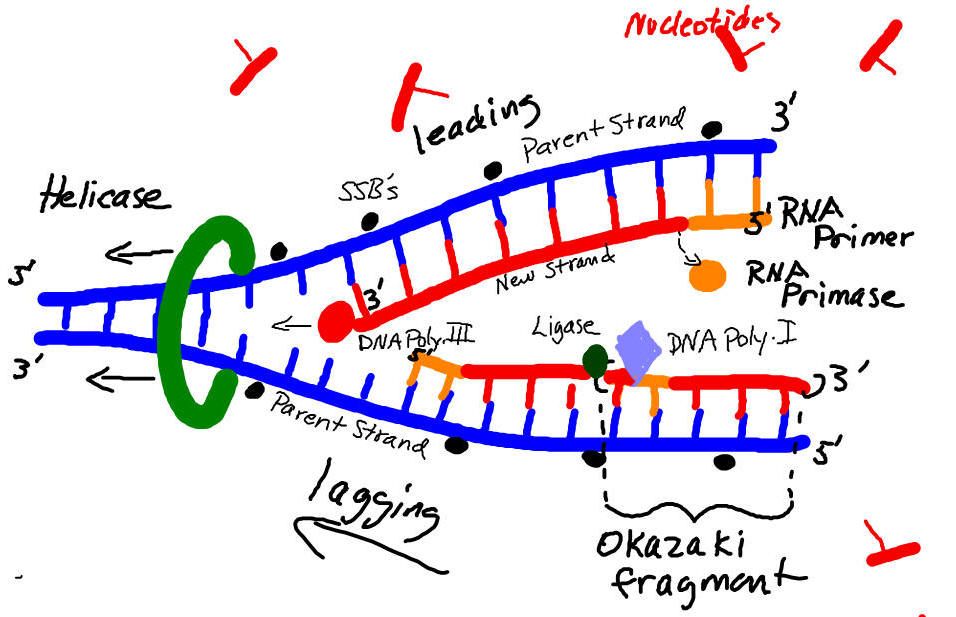
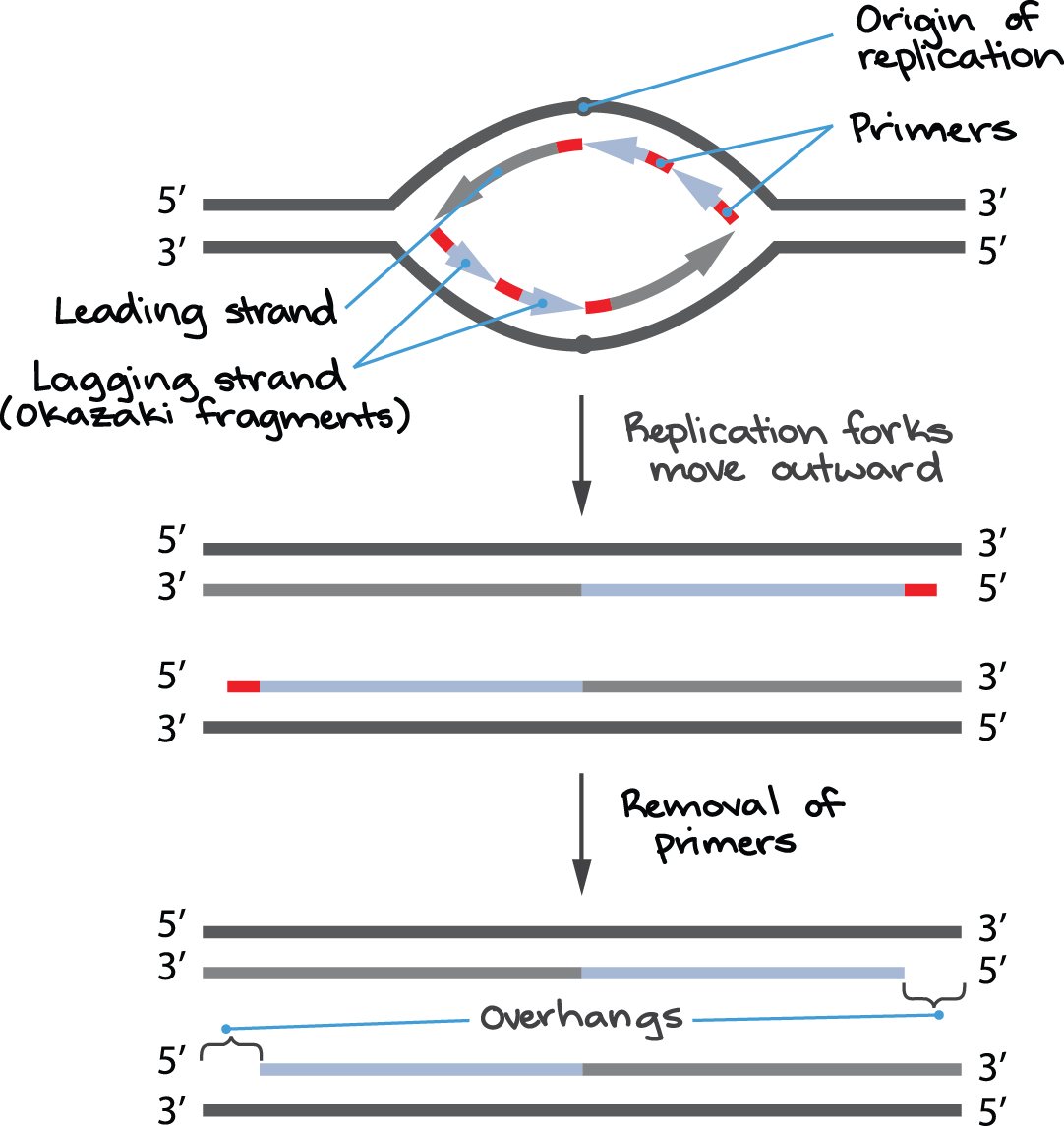
Draw Dna Replication - Prior to replication, the dna uncoils and strands separate. Notice how you retain the two original strands, but you now have two new complementary strands that don't match the original complementary strands. Why is dna replication such an important process. Web replication along the leading strand is continuous, but on the lagging strand, dna polymerase has to make the new strand in segments called okazaki fragments.then, dna polymerase i replaces the rna primers with dna nucleotides, and an enzyme called dna ligase has to connect all the fragments to create a continuous strand. It is going, let me draw a little line here, this is going in the 3' to 5' direction. We then follow dna polymerase as it copies the dna in the 5’ to 3’ direction using the existing dna as a template. A replication fork is formed by the opening of the origin of replication, and helicase separates the dna strands.an rna primer is synthesized, and is elongated by the dna polymerase. Web dna replication is a precise process where dna unwinds and splits into two strands. One strand runs from 5′ to 3′ direction towards the replication fork and is referred to as leading strand and the other strand runs from 3′ to 5′ away from the replication fork and is referred to as lagging strands.; The famous nature paper written by james watson and francis crick in 1953 entitled, 'molecular structure of nucleic acids' ends with the statement, 'it has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately. On the leading strand, dna is synthesized continuously, whereas on the lagging strand, dna is. Web some other proteins and enzymes, in addition the main ones above, are needed to keep dna replication running smoothly. The only way to replace the cells is to copy the cell’s. The first step in dna replication is the separation of the two strands by an enzyme called helicase. Web here, we will focus on dna replication as it takes place in the bacterium e. Coli for several generations in a medium containing a “heavy” isotope of nitrogen (15 n) that was incorporated into nitrogenous bases and, eventually, into the dna. The double helix unwinds and each strand acts as a template for the construction of the new dna molecule. Web this animation shows a schematic representation of the mechanism of dna replication. Prior to replication, the dna uncoils and strands separate. So this side of the ladder, you could say, it is going in the. In this article, we shall discuss the structure of dna, the steps involved in dna replication (initiation, elongation and termination) and the clinical consequences that. This process gives us two identical sets of genes, which will then be passed on to two daughter cells. Dna replication’s primary purpose is to enable living organisms to reproduce. However, the procedure is the. Web replication along the leading strand is continuous, but on the lagging strand, dna polymerase has to make the new strand in segments called okazaki fragments.then, dna polymerase i replaces the rna primers with dna nucleotides, and an enzyme called dna ligase has to connect all the fragments to create a continuous strand. The replication complex is the group of. Web some other proteins and enzymes, in addition the main ones above, are needed to keep dna replication running smoothly. Where one has a g, the other has a c; Web as previously mentioned, the location at which a dna strand begins to unwind into two separate single strands is known as the origin of replication.as shown in figure 1,. The famous nature paper written by james watson and francis crick in 1953 entitled, 'molecular structure of nucleic acids' ends with the statement, 'it has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately. A replication fork is formed by the opening of the origin of replication, and helicase separates the dna strands.an rna primer is synthesized,. This spins the incoming dna to unravel it: Translation then decodes mrna into amino acids, forming proteins essential for life functions. Web we start by seeing the dna double helix being unzipped to form a replication fork. Web this animation shows a schematic representation of the mechanism of dna replication. Dna replication’s primary purpose is to enable living organisms to. Web since the dna polymerase can only synthesize dna in a 5' to 3' direction, the polymerization of the strand opposite of the leading strand must occur in the opposite direction that the replication fork is traveling (this would be a good time to try to draw all of this, to orient yourself). Web here, we will focus on dna. Notice how you retain the two original strands, but you now have two new complementary strands that don't match the original complementary strands. Web some other proteins and enzymes, in addition the main ones above, are needed to keep dna replication running smoothly. Thus, replication cannot initiate randomly at any point in dna. This process gives us two identical sets. So this side of the ladder, you could say, it is going in the. The only way to replace the cells is to copy the cell’s. However, the procedure is the same in humans and other eukaryotes. Where one has a g, the other has a c; There were three models of replication possible from such a scheme: However, the procedure is the same in humans and other eukaryotes. Web replication along the leading strand is continuous, but on the lagging strand, dna polymerase has to make the new strand in segments called okazaki fragments.then, dna polymerase i replaces the rna primers with dna nucleotides, and an enzyme called dna ligase has to connect all the fragments to. The replication complex is the group of proteins that help synthesize the new dna strands. At ten thousand rpm in the case of bacterial systems. Web dna serves as the molecular basis of heredity through replication, expression, and translation processes. At the ends of a. Web some other proteins and enzymes, in addition the main ones above, are needed to. Web some other proteins and enzymes, in addition the main ones above, are needed to keep dna replication running smoothly. Web here, we will focus on dna replication as it takes place in the bacterium e. Web since the dna polymerase can only synthesize dna in a 5' to 3' direction, the polymerization of the strand opposite of the leading strand must occur in the opposite direction that the replication fork is traveling (this would be a good time to try to draw all of this, to orient yourself). Web we start by seeing the dna double helix being unzipped to form a replication fork. So dna replication would not be reliable. For the replication to begin there is a particular region called the origin of replication. It is going, let me draw a little line here, this is going in the 3' to 5' direction. The only way to replace the cells is to copy the cell’s. A replication fork is formed by the opening of the origin of replication, and helicase separates the dna strands.an rna primer is synthesized, and is elongated by the dna polymerase. Web dna serves as the molecular basis of heredity through replication, expression, and translation processes. The replication complex is the group of proteins that help synthesize the new dna strands. Web formation of replication fork step 2: This is the point where the replication originates. Web but after replication, you would end up with 3' atc 5' and 5' gag 3' for the first strand, and 3' acc 5' and 5' tag 3' for the other. The leading strand is constructed in a continuous fashion while the lagging strand is made discontinuously, in a series of short fragments of. So this side of the ladder, you could say, it is going in the.Dna Replication Drawing at GetDrawings Free download
Dna Easy Pictures to Draw of Dna Hall Kintalind
REPLICATION DNA Structure And Diagrams Of Dna Replication
Dna Replication Drawing Hot Sex Picture
Dna Replication Diagram With Labels
DNA Replication — Steps & Diagram Expii
5.4 DNA Replication Human Biology
Replicating The Ends Of Dna Molecules Dna Replication MCAT Content
Dna Replication Diagram With Labels
DNA Definition, Discovery, Function, Bases, Facts, & Structure
Dna Replication’s Primary Purpose Is To Enable Living Organisms To Reproduce.
The First Step In Dna Replication Is The Separation Of The Two Strands By An Enzyme Called Helicase.
The Famous Nature Paper Written By James Watson And Francis Crick In 1953 Entitled, 'Molecular Structure Of Nucleic Acids' Ends With The Statement, 'It Has Not Escaped Our Notice That The Specific Pairing We Have Postulated Immediately.
This Process Gives Us Two Identical Sets Of Genes, Which Will Then Be Passed On To Two Daughter Cells.
Related Post: